Research: Energy loss of a classroom due to open windows

The ventilation of school buildings has improved considerably over the years because the regulations for this have been tightened several times, although this has not yet been implemented in sufficient schools. The purpose of ventilation, to date, has been to provide sufficient renewal of the indoor air to prevent the concentration of undesirable components from building up. CO2 is an important component in this, which is directly dependent on the number of people in a room, their activity and the amount of air exchange.
Risk of contamination no design criterion for ventilation systems
The coronavirus has fueled the discussion about ventilation. Since ventilation systems in school buildings are not designed with the reduction of virus spread in mind, the government advises to intensify ventilation through open windows to limit the spread of the coronavirus. This applies to both old school buildings and recently built schools.
Effects of uncontrolled ventilation
Attention should be paid to the advantages and disadvantages of uncontrolled ventilation. It should be clear that the thermal comfort is not too good with this way of ventilation: in many cases it is necessary to wear a coat and a blanket to sit in the classroom. Another noticeable effect is the energy loss that this emergency ventilation entails, warm air because it goes directly outside.
Research energy loss classroom
Independent research company Climate Concept conducted research in an average classroom that included: temperature differences between indoor and outdoor, air currents, wind influence, heating capacity, return temperature, insulation, transmission loss and ventilation. With all this data and simulation models one could answer these questions:
- How much ventilation occurs with open windows?
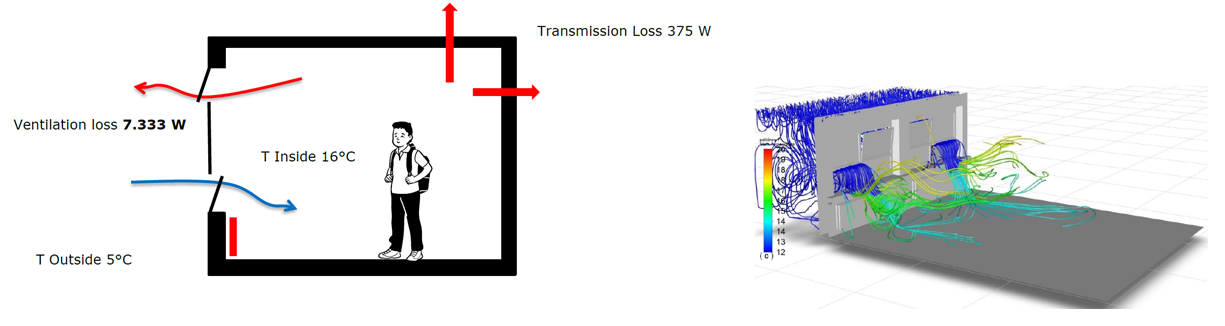
The Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation has shown that the temperature differences between inside and outside the classroom create an airflow of 2,000 m³/h (0.7 kg/s @ 5°C). This airflow occurs without the influence of wind. Wind influence can increase the airflow. - What is the maximum available heating capacity in a classroom?
The maximum available heating capacity of the radiators is: 7,881 W, at a water supply temperature of 60°C, and a return temperature of 40°C. Assuming a room temperature of 16°C. This is also the maximum achievable temperature in the room at an outside temperature of 5°C. - How much gas does the occurring ventilation cost?
6.6 m³ of gas will be consumed per day of classes (8.30 am to 5 pm) as a result of the ventilation that occurs. It is assumed that no windows are open outside the stated lesson times.
Calculation of energy costs per classroom per day
With this data we can calculate the following based on the gas rates that currently apply: If you want to keep an average of 16°C in a classroom for one lesson day, that wastes 6.6 m3/75.9 kWh of gas. This amount of energy is sent directly outside. Please note: the room is then only 16°C and therefore still needs to be heated to a comfortable temperature.
- Knowing that the Dutch gas price in September 2022 was on average € 3.83 per m3, that means a cost of € 25.27 per day, per room!
- In Belgium you currently pay an average of € 0.18 per kWh. The gas wasted per classroom per day in Belgium is € 13.66!
- In Germany you currently pay an average of € 0.28 per kWh. The gas wasted per classroom per day in Germany is € 21.30!
The solution
Save energy and make the air clean and safe: recirculate the air with an air purifier! Recirculating by means of an air purifier ensures that the air remains in the room without being reheated or need to be cooled and filtered from pollution such as particulate matter, viruses (such as flu and corona), bacteria, pollen, etc.
Example calculation of the savings “windows open” versus “clean the air”
With the calculation from this study you can calculate the gas wastage over the year. An average room with the windows open, with an average outside temperature per month and the number of effective teaching days in that month, shows us the amount of gas wasted (m3) throughout the year.
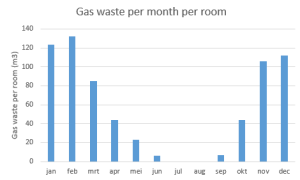
With the current energy prices, this means that a school per year, per room, wastes about 2350 euros by teaching with the windows open. With the wasted gas, the room is still only 16°C and therefore still needs to be heated to a comfortable temperature.
When we place an air cleaner in the same classroom, the windows only have to open when desired and the air is cleaned of pollution (such as corona), creating safe air. This recirculated air has no temperature loss, so it does not need to be reheated or cooled. Purchase, maintenance and energy consumption of a professional air purifier is approximately 1000 euros per year.
Would you like to read the entire study or would you like tailor-made advice? Then contact us!